All Viruses articles – Page 11
-
 News
NewsRare virus transmitted by rats infects woman in Germany—link to private pet rat breeding facility
The Seoul virus, which has been rarely detected in Germany to date and can be transmitted by rats, caused a woman to become seriously ill. Given that rats are becoming increasingly popular as pets, health experts view this as a warning sign.
-
 News
NewsNew hope for cats with eye infections: Study finds common cold sore cream safe and effective for feline use
A common human cold sore cream may soon help cats with painful eye infections: researchers found that 1% penciclovir cream (Fenlips®), when applied to cats’ eyes, was safe, well-tolerated, and maintained antiviral levels for over eight hours.
-
 News
NewsMosquito saliva may hold clues to fighting chikungunya inflammation
Scientists have uncovered a surprising mechanism showing how mosquito saliva can alter the human body’s immune response during chikungunya virus (CHIKV) infection - it not only transmits the virus but also influences how the body’s immune system responds.
-
 News
News’Footprint of Death’ gives new clues to cell life, spread of disease
Scientists at La Trobe University have discovered a previously unknown way viruses could spread around the body, potentially paving the way for more effective drug development. Source: La Trobe University Dead cells after the self-destruction and fragmentation process. The large green areas are the “eat me” signals ...
-
 News
NewsNew antivirals could help prevent cold sores by changing cell structures
A class of antivirals called Pin1 inhibitors could reduce or stop outbreaks of herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1), the common infection behind oral herpes, according to new research.
-
 News
NewsIn the midst of a global dengue epidemic, Wolbachia kept a Brazilian city safe
In the middle of the world’s worst global dengue epidemic, a city in Brazil was effectively protected by an innovative program that introduced the bacterium Wolbachia into the local mosquito population, lowering the rate of dengue by almost 90 per cent.
-
 News
NewsWhat we know and what we need to know about Antarctic marine viruses
Antarctic marine viruses, while proven to be important players in the ecosystem, are not completely understood. In a new paper, researchers aim to fill in the gap between what is known and what is unknown, with a primary focus on RNA viruses, the influence of climate change and their implications.
-
 News
NewsDiscovery of hundreds of new human gut viruses provides a new approach to studying the gut microbiome
Hundreds of new viruses living inside bacteria within our gut have been discovered in an international study. These bacteriophages could eventually be used to reshape the gut microbiome, potentially influencing gut health and the progression of various disease states.
-
 News
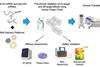
NewsHuman Organ Chip technology sets stage for pan-influenza A CRISPR RNA therapies
Human lung alveolus chip infection model enables investigation of viral replication, inflammatory responses, and genetic off-target effects of a novel pan-influenza CRISPR therapy.
-
 News
NewsBreakthrough in coronavirus fight: scientists develop powerful bispecific inhibitor to combat a wide range of coronaviruses
Researchers have discovered a powerful bispecific inhibitor capable of combating all existing human-pathogenic coronaviruses, including those resistant to existing treatments like Paxlovid.
-
 News
NewsCould cardamom seeds be a potential source of antiviral treatment?
Researchers have found that cardamom seed extract, as well as its main bioactive ingredient, 1,8-cineole, can have potent antiviral effects through its ability to enhance the production of antiviral molecules known as type I interferons via nucleic acid ‘sensors’ inside cells.
-
 News
NewsSafer, more effective vaccines with new mRNA vaccine technology
A new messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) vaccine technology could make future vaccines safer, more effective, and less burdensome for patients. The new approach uses albumin-recruiting lipid nanoparticles to deliver mRNA precisely to lymph nodes while bypassing the liver.
-
 News
NewsTraditional Chinese medicine combined with peginterferon α-2b in chronic hepatitis B
A new study demonstrates that adjunctive Traditional Chinese Medicine significantly enhances the antiviral efficacy of peginterferon α-2b in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B while concurrently mitigating treatment-limiting myelosuppression.
-
 News
NewsResearchers developing new easy-to-use viral biosensor test, giving patients more accurate and immediate results
An interdisciplinary team of researchers is creating a single low-cost test to detect HIV & Hepatitis B and C simultaneously, that may be used in resource-limited settings. With quicker and more accessible results, the test has potential to save lives.
-
 News
NewsCHIKVdb: A comprehensive genomic resource for chikungunya virus surveillance and outbreak response
Scientists have developed the Chikungunya Virus Database (CHIKVdb), a comprehensive genomic resource. CHIKVdb integrates 8,193 nucleotide sequences and 10,637 protein sequences from five major host categories across 99 countries, spanning 40 years.
-
 News
NewsWHO upgrades its public health intelligence system to boost global health security
The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched version 2.0 of the Epidemic Intelligence from Open Sources (EIOS) system, used globally for the early detection of public health threats.
-
 News
NewsMaldives is first country to achieve ‘triple elimination’ of mother-to-child transmission of HIV, syphilis and hepatitis B
The World Health Organization has validated the Maldives for eliminating mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B, while maintaining its earlier validation for EMTCT of HIV and syphilis. This makes the Maldives the first country in the world to achieve ‘triple elimination’.
-
 News
NewsMeasles immunity 90% in BC’s Lower Mainland
In British Columbia’s Lower Mainland, 90% of people have detectable antibodies against measles, indicating high vaccine coverage and population protection, according to a new study.
-
 News
NewsTwo-dose recombinant shingles vaccine is effective even accounting for prior receipt of live shingles vaccine
A target trial emulation was conducted to assess the effectiveness of recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) accounting for prior receipt of live zoster vaccine (ZVL) and immunocompetence. The results suggest individuals vaccinated with ZVL should be revaccinated with two doses of RZV.
-
 News
NewsStudy finds HEPA purifiers alone may not be enough to reduce viral exposure in schools
In a secondary analysis of a study of 200 classrooms, researchers found respiratory viral exposures were still high in those with HEPA purifiers, suggesting additional interventions are needed.
