Valneva SE, a specialty vaccine company, has announced that the company has decided to voluntarily withdraw the biologics license application (BLA) and Investigational New Drug (IND) application for its chikungunya vaccine, IXCHIQ® , in the United States, following suspension of the license by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in August 2025.
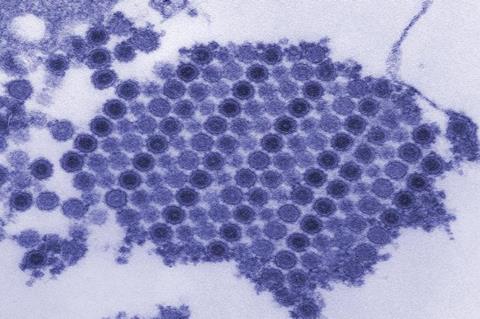
The Company had been awaiting further information with respect to its formal response to the vaccine license suspension. Valneva was recently informed of the FDA’s further decision to now place the Investigational New Drug (IND) on clinical hold pending an investigation of a newly reported foreign Serious Adverse Event (SAE).
There are currently no clinical studies involving IXCHIQ® that are actively vaccinating participants, and the Company intends to move forward with its planned post-marketing clinical activities, subject to further discussions with relevant regulatory authorities. The SAE occurred outside of the U.S. and involved a younger adult who received three concomitant vaccines, including IXCHIQ® .
READ MORE: Valneva reports high sustained immune response in adolescents one year after Chikungunya Vaccine
READ MORE: Vaccine created to prevent dangerous tropical disease receives FDA approval
Based on the information made available to Valneva, which the company submitted to the U.S. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) as well as to all other pharmacovigilance systems in accordance with the products license, the case may be plausibly related to IXCHIQ® vaccination, but causality has not been determined. The Company is actively seeking additional information to further characterize the case.
Valneva said it is committed to upholding the highest safety standards, and the company continues to engage proactively with health authorities in all territories where IXCHIQ® is licensed, including Europe, Canada, the United Kingdom and Brazil.
While IXCHIQ® is currently focused on travelers to regions where the virus is endemic, such as tropical and subtropical areas in Asia, Africa, and the Americas, and persons for whom vaccination is medically justified based on risk in accordance with the approved label and vaccination guidance, the company continues to believe that IXCHIQ® ’s benefit-risk profile also remains favorable for people living in the endemic and outbreak settings, where IXCHIQ® may be uniquely positioned as a highly durable single-shot vaccine.
About Chikungunya
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is a mosquito-borne viral disease spread by the bites of infected Aedes mosquitoes which causes fever, severe joint and muscle pain, headache, nausea, fatigue and rash. Joint pain is often debilitating and can persist for weeks to years.
In 2004, the disease began to spread quickly, causing large-scale outbreaks around the world. Since the re-emergence of the virus, CHIKV has now been identified in over 110 countries in Asia, Africa, Europe and the Americas. Between 2013 and 2023, more than 3.7 million cases were reported in the Americas and the economic impact is considered to be significant.
The medical and economic burden is expected to grow with climate change as the mosquito vectors that transmit the disease continue to spread geographically. As such, the World Health Organization (WHO) has highlighted chikungunya as a major public health problem.





No comments yet