From ambassadorship to action: Leading a national scientific writing and publishing workshop in the UK
Medical Microbiologist and Antimicrobial Resistance Researcher Dr. Oluwole Owoyemi, ASM Young Ambassador to the UK, reveals why he designed a scientific writing and publishing workshop for early career scientists - and how it went.
- Previous
- Next
Gut microbiome and obesity: what we know - and what we don’t
Dysbiosis is defined as an imbalance in the composition and function of the gut microbiota. This imbalance can lead to dysregulated interactions within the bacterial community and between microbes and the host, and it can be associated with disease states. However, discussions of dysbiosis often rely on simplified dichotomies, such ...
Read storyFrom Petri dishes to chips: what can microbiology learn from microfluidics?
Microfluidics is a fast-growing field focused on manipulating tiny volumes of fluid, often within channels no wider than a human hair. Despite its potential, around 90% of microbial experiments are still carried out under static conditions. So, what are we missing by ignoring flow? And how can microfluidics help close the gap?
Unlocking the secrets of phages: DNA modification discoveries offer new weapons against antimicrobial resistance
Bacteria and their viral predator bacteriophages (phages) have coevolved for billions of years and are engaged in an endless arms race against each other. DNA modifications are among the most widespread defenses to block bacterial RM and CRISPR-Cas systems.
The smell of the sea: how microbes shape Earth’s sulfur story
That distinctive “sea breeze” scent we associate with the coast isn’t just nostalgia; it’s the smell of microbial chemistry at work. Behind it lies an intricate web of microbial pathways turning sulfur compounds into gases that help shape Earth’s climate.
Under the Lens video series
The Microbiologist: Under the Lens | Episode 2
The Microbiologist: Under the Lens | Episode 1
Get unlimited access to The Microbiologist
The Microbiologist provides detailed information on the latest research, topics, reviews, events and news on a wide variety of microbiological topics.
Members of Applied Microbiology International get unlimited access as a benefit. Find out more about AMI Membership
Listeria: the inconvenient truth that shaped our industry
Director General of the Chilled Food Association, Karin Goodburn MBE, who sits on AMI’s Food Security Advisory Group, reveals why the publication of new Listeria guidance for the UK food industry is regarded as a landmark moment.
We couldn’t get people interested in science - until we started speaking their language
In 2020, Puerto Rico faced a misinformation crisis. Melanie Ortiz Alvarez De La Campa reveals how five STEM undergraduates created a sci-comm organization that helped pass legislation, educated thousands, and created an inclusive database of Caribbean scientists.
The politics behind the global divide in bacteriophage therapy
The therapeutic potential of bacteriophages (or ‘phages’) has been widely dismissed for decades in the West, despite being regularly used to treat patients worldwide in the early and mid-20th century. In an age rife with disinformation, can the true potential of clinical phage technology be communicated to a public already uneasy about scientific intervention?
The National Collection of Pathogenic Viruses (NCPV): a critical resource for virology and public health
It’s now 25 years since the National Collection of Pathogenic Viruses (NCPV) was founded as a dedicated, secure, and relevant national virus repository for the UK. Jane Burton, Teresa Ramalho and Tilly Maybery explore how the collection has evolved - and is tackling future global health concerns.
A day in the life of a soil microbial ecologist
Dr. Taniya RoyChowdhury, a soil microbial ecologist and biogeochemist at the Woodwell Climate Research Center, describes a typical day.
Scientific Event Travel Grant: how the Safepork conference surpassed my expectations
Shan Goh from the University of Hertfordshire reports back on the International Symposium on the Epidemiology and Control of Biological, Chemical and Physical Hazards in Pigs and Pork held in Rennes, France, in October. Shan was supported with a Scientific Event Travel Grant awarded by AMI.
Team finds E. coli, other pathogens in Potomac River after sewage spill
Following one of the largest sewage spills in U.S. history, researchers detected high levels of fecal-related bacteria and disease-causing pathogens in the Potomac River, raising urgent public health concerns and underscoring the risks posed by aging sewer infrastructure.
Researchers on the cusp of a vaccine for a global health threat
Researchers are on the cusp of a new vaccine to prevent chikungunya, a global health threat which attacks human joint tissue. The team tested whether they could engineer E. coli to assemble biopolymer particles which displayed chikungunya antigens and performed as a vaccine.
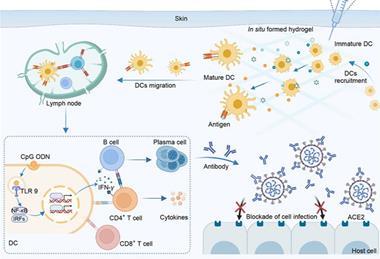
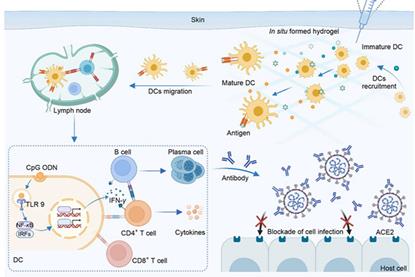
Construction of a localized immune niche via supramolecular hydrogel vaccine to elicit durable and enhanced immunity against infectious diseases
A new article discusses the construction of a localized immune niche via supramolecular hydrogel vaccine to elicit durable and enhanced immunity against infectious diseases.
Food security
CARB-X to support development of typhoid fever diagnostic from Chembio
CARB-X is awarding US$1.8 million to Chembio Diagnostic Systems, Inc. to develop a rapid point-of-care test for the detection of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibodies to diagnose acute infection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.
Clean Water
Team finds E. coli, other pathogens in Potomac River after sewage spill
Following one of the largest sewage spills in U.S. history, researchers detected high levels of fecal-related bacteria and disease-causing pathogens in the Potomac River, raising urgent public health concerns and underscoring the risks posed by aging sewer infrastructure.
New study reveals cyanobacteria may help spread antibiotic resistance in estuarine ecosystems
Scientists have discovered that cyanobacteria may play a major role in spreading antibiotic resistance genes in coastal environments. The findings highlight a previously overlooked link between natural nutrient cycling and the global challenge of antibiotic resistance.