All Disease Treatment & Prevention articles – Page 6
-
 News
NewsTo treat long COVID, we must learn from historical chronic illnesses, medical researchers say
Scientists and doctors have highlighted the importance of studying long COVID in the context of other post-acute infection syndromes or chronic illnesses. By analyzing historical accounts of other epidemics, researchers can gain important perspective on the effects of these chronic illnesses.
-
 News
NewsThe power of gut enzymes: why healthy eating affects everyone differently
Researchers have uncovered a mechanism that determines how our gut microbiome processes healthful plant compounds. The chemical cookbook of gut bacteria varies from person to person—and is often disrupted in chronic diseases.
-
 News
NewsFamily dogs boost adolescent mental health through the microbiome
It’s no surprise that dogs benefit people’s mental health. Researchers point to a reason as to why: dogs prompt changes in the collection of microbes that live in and on our bodies, resulting in an increase in mental health.
-
 News
NewsMetabolites produced in the intestine play a central role in controlling obesity and diabetes
A study has identified a group of metabolites that travel from the intestine to the liver and then to the heart, where they are pumped throughout the body. These metabolites play an important role in controlling metabolic pathways in the liver and insulin sensitivity.
-
 News
NewsHospital infections associated with higher risk of dementia
A large-scale meta-analysis shows that adults hospitalized with infections have a significantly higher risk of developing dementia. Among the types of infections studied, sepsis carried the highest risk, followed by pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin or soft tissue infections.
-
 News
NewsPrebiotic in diet linked to less impulsivity in gambling rats with traumatic brain injury
Using a prebiotic to influence bacterial activity in the gut after a traumatic brain injury may help reduce impulsive behavior, one of the common symptoms to follow a moderate blow to the head, a new study in rats suggests.
-
 News
NewsGut microbiome connects obesity to cancer, impacting public health
A new review highlights growing scientific evidence that imbalances in gut bacteria can influence metabolism, trigger inflammation, and increase cancer risk. These insights offer new possibilities for disease prevention, early detection, and personalized health care.
-
 News
NewsNatural, non-engineered bacterium selectively targets colorectal cancer
Scientists have demonstrated that the marine bacterium Photobacterium angustum exhibits potent antitumor effects against colorectal cancer. The natural bacterium requires no genetic modification yet selectively accumulates in tumor tissues with minimal impact on healthy organs.
-
 News
NewsToxic gut bacteria may drive ulcerative colitis by killing protective immune cells
A toxin-secreting gut bacterium may fuel ulcerative colitis by killing protective immune cells that maintain intestinal homeostasis, according to a new study. The findings suggest potential for new treatment strategies.
-
 News
NewsRebalancing lung repair with immune damage is key to surviving severe influenza
Recovery from deadly influenza infection may hinge on helping the lungs heal in addition to stopping the virus, according to a new study in mice, which shows that pairing modest antiviral therapies with immune modulation can restore damaged tissues and lung function, even after severe infection has taken hold.
-
 News
NewsBacteria ‘pills’ could detect gut diseases — without the endoscope
Researchers report that they’ve developed a sensor made of tiny microspheres packed with blood-sensing bacteria that detect markers of gastrointestinal disease. Taken orally, the miniature “pills” also contain magnetic particles that make them easy to collect from stool. Excreted from mouse models with colitis, the bacterial sensor detected gastrointestinal bleeding within minutes.
-
 News
NewsTraces of bacteria inside brain tumors may affect tumor behavior
Scientists have uncovered unexpected traces of bacteria within brain tumors. This discovery offers new insights into the environment in which brain tumors grow and sets the stage for future studies seeking to improve treatment outcomes.
-
 News
NewsNext-generation microbiome medicine may revolutionize the treatment of Parkinson’s and similar disorders
Scientists have engineered the probiotic bacterium Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 as a drug-delivery system that continuously produces and delivers the gold-standard Parkinson’s drug Levodopa, which is converted to dopamine in the brain. E. coli Nissle strain was chosen for its century-long record of safely treating gastrointestinal disorders in humans.
-
 News
NewsNew DNA analysis approach could transform understanding of disease evolution
By adapting techniques originally used to study ancient DNA from archaeological specimens, researchers were able to recover genetic information from nearly century-old medical samples.
-
 News
NewsThe link between the gut microbiome and autism is not backed by science, researchers say
There’s no scientific evidence that the gut microbiome causes autism, a group of scientists argue in an opinion paper. They warn that conclusions that supported this hypothesis are undermined by flawed assumptions, small sample sizes, and inappropriate statistical methods.
-
 News
NewsScientists find way to find the gut microbiome into a longevity factory
A team of researchers has found a way to turn the bacteria living in the digestive tracts of animals into factories that can produce compounds that promote longevity in their hosts—showing a potential new drug development strategy.
-
 News
NewsScientists tie lupus to a virus nearly all of us carry
The Epstein-Barr virus is directly responsible for commandeering what starts out as a minuscule number of immune cells to go rogue and persuade far more of their fellow immune cells to launch a widespread assault on the body’s tissues, a study has shown.
-
 News
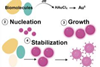
NewsScientists harness algae for a greener way to create functional gold nanoparticles
Researchers have pioneered a novel, sustainable method for synthesizing functionalized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using microalgae. This approach not only avoids the harsh chemicals used in conventional methods but also produces AuNPs that are more stable and less toxic to healthy cells.
-
 News
NewsHuman PARP gene could be novel target for viral diseases or immune-mediated disorders
Researchershave discovered a human gene, the protein PARP14, plays a role in regulating interferon, part of the body’s innate immune system. Their study could guide development of antiviral therapies for several groups of viral infection.
-
 News
NewsSingle-cell insights reveal how HPV status reshapes penile tumor immunity
A study found that HPV-positive tumors in penile squamous cell carcinoma cases contained fewer proliferative macrophages and less exhausted CD8+ T cells, along with stronger chemokine signaling, revealing distinct immune remodeling associated with HPV infection.
